Last Updated on May 25, 2022 by Neera Bhardwaj
In India, the tax structure is divided into direct and indirect taxes levied by the Central and State Governments. Corporate entities and individuals must pay direct taxes on their taxable income and deposit their taxes. On the other hand, the sale and provision of goods and services call for the levy of indirect taxes.
The income tax is one of the major central taxes in India. It is a direct tax that the Central Government levies and collects. Let’s explore this tax regime in detail.
Table of Contents
What is income tax in India?
The income that individuals and businesses generate in a financial year is liable for taxation, known as Income Tax. The Income Tax Act, 1961, is the statute that guides the administration, levy, collection, and recovery of income tax in India. It contains elaborate chapters, each dealing with particular aspects of taxation. The Finance Minister of India presents the Annual Budget, bringing amendments to make the Act more comprehensive and inclusive.
Who is liable to pay income tax?
The Income Tax Act classifies taxpayers into distinct categories with different tax rates applicable for each. The categories are as follows:
- Individuals
* Residents
* Non-residents - Hindu Undivided Families (HUF)
- Body of Individuals (BOI)
- Association of Persons (AOF)
- Firms
- Companies
Types of income liable for taxation
The Income Tax Department lays down five income heads that are subject to income tax. These are:
- Income from salary
- Income from house property
- Income from business or profession
- Income from capital gains
- Income from other sources (including fixed deposits, savings bank account interests, lotteries, etc.)
What is an income tax return (ITR)?
Income Tax Return (ITR) is a form for reporting the taxable income, tax liability, and claiming any tax deduction. It is mandatory for salaried and self-employed individuals, HUFs, firms, and companies to file IT returns to the Income Tax Department of India. If your income is eligible for taxation, the next step is to file an ITR.
What is ITR filing?
ITR filing is the process by which you, as a taxpayer, will file a report of your total income in a financial year. With a few exceptions, online filing of ITR is mandatory for all taxpayers within a prescribed deadline. You can file your ITR for a financial year through the Government’s Income Tax e-Filing Portal.
Eligibility for income tax filing
Individuals fulfilling any of the following criteria have to file ITR:
- As per age group and gross annual income:
| Age of individuals | Gross annual income |
| Below 60 yrs | More than Rs. 2.5 lakh |
| 60-80 yrs | More than Rs. 3 lakh |
| Above 80 yrs | More than Rs. 5 lakh |
- Individuals earning income from house property or other sources
- Individuals earning from or investing in foreign assets
- Individuals applying for a loan or visa
- Firms and companies, regardless of the profit or loss
- Individuals claiming a refund from the Income Tax Department
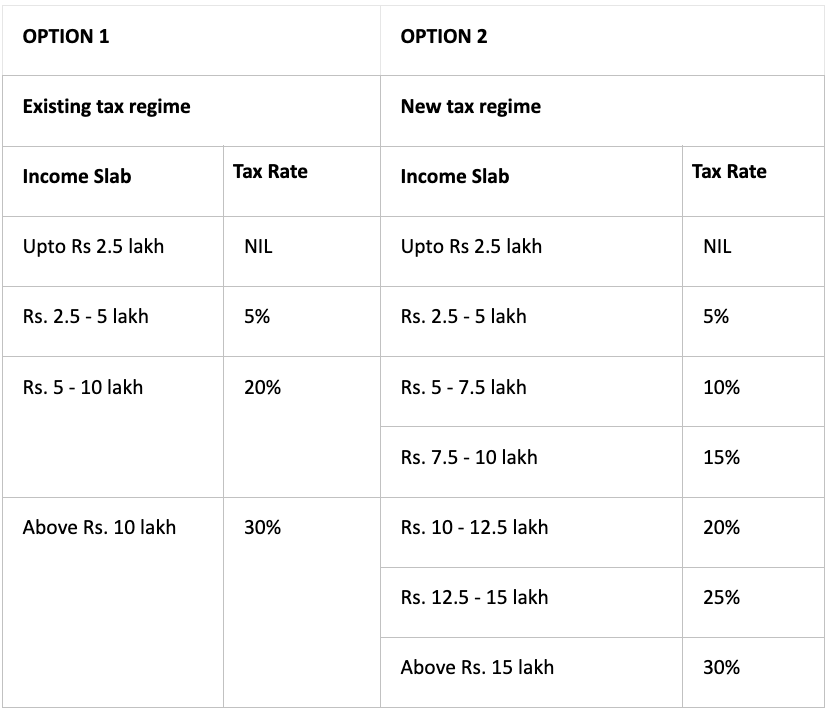
Income tax slabs for AY 2021 – 2022
You can opt for the existing tax regime or the new tax regime. While the latter has lower taxation rates, you will not be allowed certain deductions and exemptions the old regime offers.
The slabs for both the existing and new tax regimes are as follows:
1. Age group: Less than 60 yrs
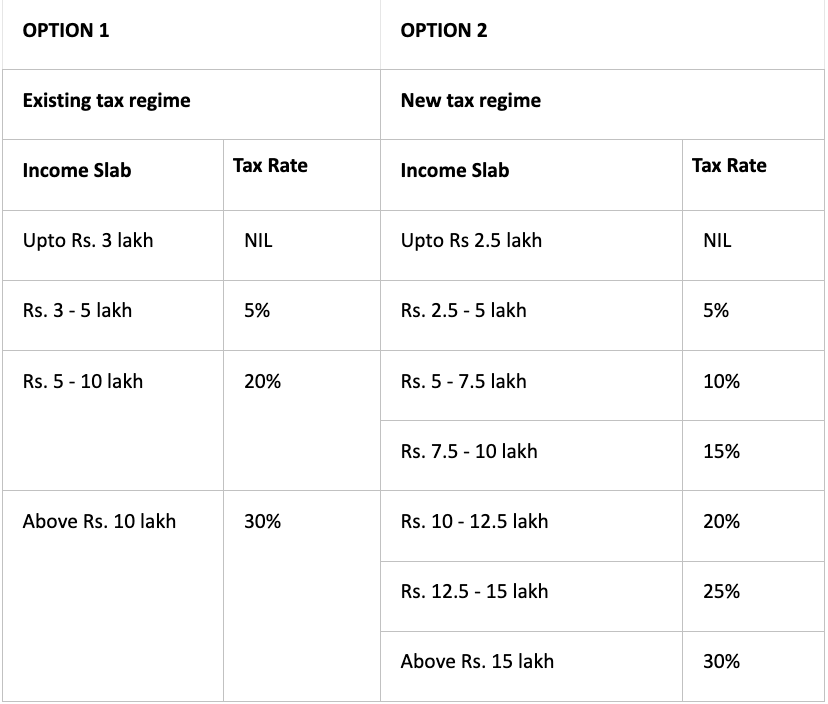
2. Age group: 60+ yrs
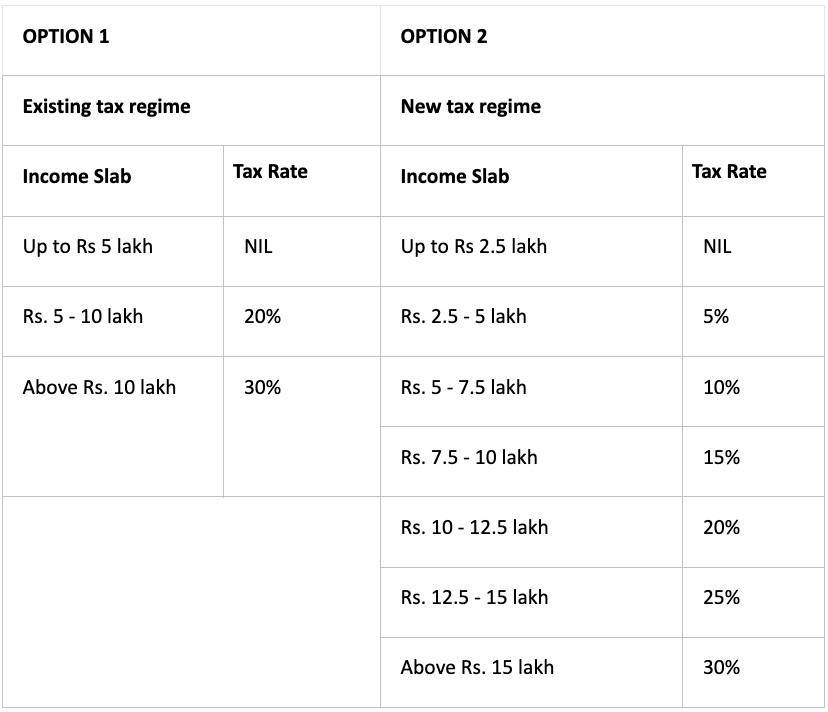
3. Age group: 80+ yrs
Documentation required for ITR filing
You need to collect the following documents for e-filing ITR:
- Payslips/salary slips
- PAN Card
- AADHAR Card
- Bank statements
- Form 16
- Form 26AS
- Interest certificates
- Proof of tax deduction documents as applicable
Besides, the Income Tax Department prescribes seven types of ITR forms depending on the taxpayer’s type of income. Therefore, before e-filing your ITR, you must choose the form applicable to you. The ITR forms are ITR-1, ITR-2, ITR-3, ITR-4, ITR-5, ITR-6, and ITR-7.
Procedure for e-filing ITR
Given below is a step-by-step overview of how to e-file your ITR through the online government portal:
- Visit the official e-filing portal of the Income Tax Department.
- Register yourself if you are a new user or login if you are an existing user.
- Click on ‘File Income Tax Return’ under the e-file tab.
- Select the necessary details on the Income Tax Return Page and click ‘Continue.’
- Fill in the mandatory fields in the online ITR form.
- Choose any verification option from the ‘Taxes Paid and Verification’ tab.
- Click on ‘Preview and Submit’ and verify your entered data.
- Submit the ITR.
Once the online process is complete, the next step is verification as per the mode you chose.
Conclusion
As a citizen of India, it is imperative that you pay your share of taxes. You must file an ITR stating your details and tax liabilities based on your income category. Before doing so, ensure you are familiar with the documentation, ITR forms, and e-filing process. You will have to pay hefty penalties if you fail to file your ITR within the due date. The GOI has again extended the due date to file taxes until 15 March 2022. Reach out to your CA or tax advisor for timely filing and professional guidance on taxes
- Top Fund of Funds (FOF) in India – Full Form, Types & More - Mar 28, 2025
- Bond Funds – Meaning, Types, Risks, and Benefits - Mar 27, 2025
- Money Market Mutual Funds: Meaning, Benefits, Liquidity and Taxation - Mar 13, 2025