Last Updated on May 25, 2022 by Neera Bhardwaj
Paying taxes is one of the primary responsibilities of a citizen. For salaried individuals, paying income taxes might seem dreadful considering the significant chunk of earnings that come under taxable income. But strategizing your finances to make use of the income tax exemption and deductions could substantially reduce your tax liability.
Income tax exemptions/allowances are components of your gross salary exempt from your total taxable income. These include HRA, LTA, and children’s education allowance, among others. On the contrary, income tax deductions arise from various investment instruments and expenses incurred in a particular financial year. Such expenditures are balanced against your gross annual income while filing ITR.
Both income tax exemption and deduction help you save tax by lowering your overall tax liability. Let’s explore these exemptions and deductions in more detail.
Table of Contents
Income tax exemptions for salaried employees 2021-22
The Income Tax Act, 1961, mandates certain income tax allowances/exemptions for the salaried class. These exemptions, thus, can help salaried individuals save a significant amount of their income.
Here is a list of some of the major income tax exemptions as per Section 10 of the Act:
House rent allowance (HRA)
You can get the benefit of HRA if you have rented accommodation. You can claim the minimum of the following as HRA exemption:
- Total HRA received
- 40% of income (Basic + DA) for non-metro residents and 50% for those living in metro cities
- Actual monthly rent minus 10% of salary (Basic + DA)
Leave travel allowance (LTA)
The Income Tax Act grants salaried employees exemption on domestic travel expenses by railways, air, or other public transport. However, it does not include expenditures on food, shopping, entertainment, or other leisure activities.
You can use the LTA exemption twice in four years.
Standard deductions
Since the Union Budget of 2019, salaried individuals can claim a flat standard deduction of Rs. 50,000. This is a replacement for the medical reimbursements and transport allowance.
Child education allowance
If your employer provides you with a children’s allowance, you can claim a maximum of Rs. 100 tax exemption monthly. This exemption is applicable for up to two children.
Relocation allowance
If you have to shift to a new location for work/business purposes, your employer will bear the related expenses. These include accommodation, packaging charges, car transportation costs, and train/air tickets, among others. Such expenses that your employer reimburses or pays for are directly exempt from tax.
Mobile reimbursement
You can claim reimbursement of mobile and telephone use expenses at your residence. Such reimbursement can be the amount given in the salary package or the actual bill amount, whichever is lower.
Income tax deductions for salaried employees 2021-22
Section 80 of the Income Tax Act allows several tax deductions to salaried employees. Let’s look at some of these tax-saving deductions:
Section 80C
Only individuals and HUFs can avail of a maximum tax deduction of Rs. 1.5 lakh annually from their total income. Some of the tax-saving investment instruments under Section 80C include:
- Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF)
- Life insurance premium
- Equity-Linked Savings Scheme
- Principal payment on home loans
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
- Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS)
- National Saving Certificate (NSC)
- Annuity/Pension schemes
- Tax-saving fixed deposits
- Infrastructure bonds
Section 80D
Section 80D deals with tax deductions you can claim on medical expenses for yourself, your family, and your parents.
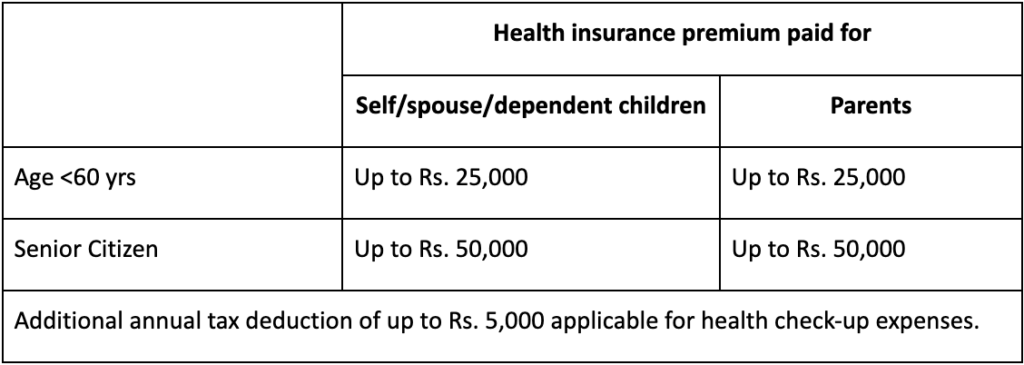
Section 80E
If you’ve taken an education loan for higher studies, the interest for the same is claimable for tax deduction under Section 80E. However, the claim is valid only for eight years. You can start claiming from the year the loan repayment begins for the next seven years or until full repayment, whichever is earlier.
Section 80EE
If you’ve taken a home loan, you can claim a tax deduction of up to Rs. 50,000 on its interest. However, the loan amount should not exceed Rs. 35 lakh. In addition, the value of the property should be Rs. 50 lakh or less.
Section 80G
If you’re making contributions to charitable organisations or relief funds, you can claim tax deduction under Section 80G. However, you can claim such a deduction only if you have made donations to prescribed funds.
Also, any cash donation exceeding Rs. 2,000 is not claimable for deduction under Section 80G.
Section 80TTA
Under Section 80TTA, you can claim tax deductions of up to Rs. 10,000 on income earned as interest. Only individuals and HUFs can avail this claim on the interest income from savings accounts. Interest amounts exceeding Rs. 10,000 will be taxable.
Section 80TTB
Under this section, senior citizens can claim a tax deduction of a maximum of Rs. 50,000. Such deductions apply to their total gross income in a financial year.
Section 80U
Individuals suffering from at least 40% disability can claim tax deductions, provided such disability is certified by a medical authority. Tax deductions of up to Rs. 75,000 and Rs. 1.25 lakh are applicable for disabilities and severe disabilities, respectively.
Deductions and exemptions not claimable under the new tax regime
The new tax regime doesn’t allow 70 deductions and exemptions, some of which are listed below:
- House Rent Allowance
- Leave Travel Allowance
- Children education allowance
- Investments under Section 80C
- Income for senior citizens under Section 80TTB
- Interest income under Section 80TTA
- Donations under Section 80G
- Education loan interest
- Housing loan interest payments
- Cost of medical expenses of self or dependent
The bottom line
Before you start preparing for your annual ITR filing, make sure you have a thorough understanding of the various tax-saving instruments. Be it allowances/exemptions or deductions on different expenses; you have a gamut of opportunities to save tax money. While the new tax regime offers lower tax rates, it drops several exemptions and deductions that the existing one provides. The tax regime you choose is an entirely personal decision.
Regardless of choice, calculate the tax-exempt components of your salary and assess the total deductions you are eligible to claim. Reach out to your CA or tax advisor for professional advice on taxes.
- How To Declare Mutual Funds in ITR & Disclose Capital Gains in India? - Jun 6, 2025
- How To Sell or Exit Your Mutual Funds in India? - Jun 6, 2025
- Fund of Funds (FOF): Meaning, Types & Advantages - May 13, 2025





