Listed companies usually share a part of their profits with their shareholders. This is called a dividend. The dividend depends on the profits the business earns and the management’s decision to distribute a portion of it. The Dividend Per Share (DPS) is an important metric to consider when investing in a company. So, let’s understand what it is, its formula, and more.
You will Learn About:
What is dividend per share?
.png)
Dividend per share is the aggregate dividend that a company has paid per unit of its outstanding shares. It tells investors the quantum of dividends they would receive from the company for every unit of share held.
DPS includes all types of dividends that a company may pay to its shareholders, like interim dividends and final dividends. However, special dividends are excluded from DPS. Moreover, the DPS is calculated for a particular period, like a quarter or a year. Typically, companies share the DPS through financial statements and also in their communication to shareholders.
Return on equity: Highlights
- A dividend per share is the dividend paid by a company per unit of outstanding shares within a specified period.
- DPS is calculated by dividing the dividend paid with the outstanding shares or by multiplying the EPS and the dividend payout ratio.
- A high DPS means more income for investors. It also means higher profitability and helps the company increase its market perception.
How to calculate dividend per share?

The formula for calculating the DPS is as follows –
DPS = Aggregate dividends paid / Total number of outstanding shares
There is an alternative formula, too, for calculating the DPS. It is as follows –
DPS = Earnings per share * Dividend payout ratio
Types of dividends
A company can give out different types of dividends to its customers. These include the following –
- Special dividends
Special dividends are those that are not distributed in the normal course of business. However, if the company makes a windfall profit and wants to reward its investors, it can pay out a special dividend. Special dividends are not fixed. They are usually a one-off affair, and a company can decide not to declare such dividends.
- Interim dividends
Interim dividends are paid (during a financial year) when the company has not prepared its final financial statements. If the company believes that the financial year is going well and it has accumulated considerable profits, it can pay out interim dividends to its shareholders.
- Final dividends
Final dividends are those that a company declares after the financial statements of a financial year are prepared. From the financial statements, the company can check its annual profits and pay a part of such profits in the form of dividends.
Dividend per share example
Here are some common examples of DPS calculations –
If a company has 10,000 outstanding shares and it pays out an aggregate dividend of Rs. 200, the DPS would be Rs. 50.
Assume a company has an authorised share capital of 1 lakh shares, each priced at Rs. 10. It has issued 50,000 shares. In a year, the company earned an aggregate profit of Rs. 20 lakh. The company distributed 50% of its profit as dividends. In this case, to calculate the DPS, the steps are as follows –
– Outstanding shares – 50,000
– Dividend distributed – 50% of profits = 50% of Rs. 20 lakh = Rs. 10 lakh
– DPS = Rs. 10 lakh / 50,000 = Rs. 20
Thus, the company paid a dividend of Rs. 20 per share to its shareholders.
Calculating DPS from the income statement
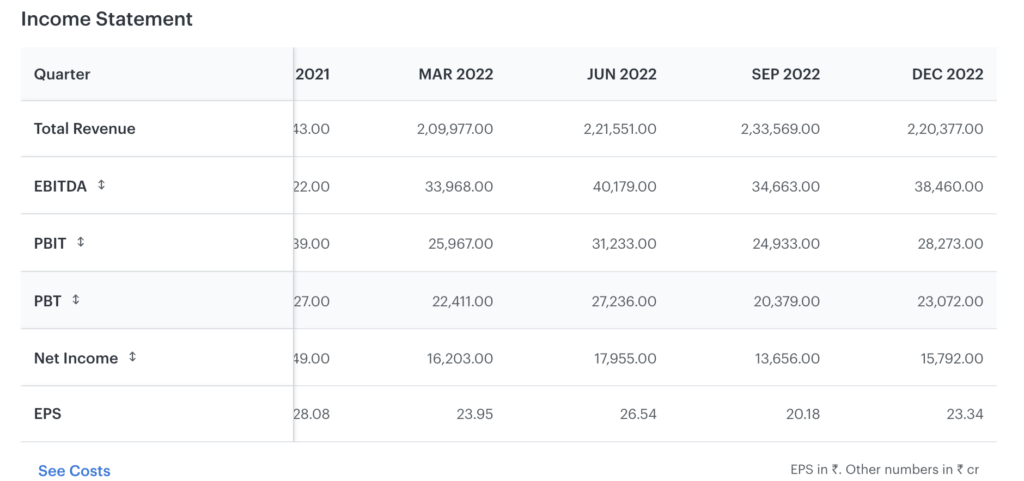
The income statement of a company can also help you calculate the DPS using the alternative dividend per share formula.
However, the calculation of the DPS from the income statement is possible if the company has had a consistent dividend payout ratio over the past years. A consistent ratio depicts that the company may pay a similar percentage of dividend in the current year too.
To calculate the DPS from the income statement, the steps are as follows –
- Find out the net income or profit earned by the company from the income statement.
- Check the number of outstanding shares (issued shares) on the balance sheet.
- Divided the net income with the outstanding shares, and you would get the EPS (Earnings Per Share).
- Now, multiply the EPS with the dividend payout ratio, and you would get the DPS.
Interpreting dividends per share – High vs Low
A high DPS is usually a good sign, both for investors and for companies. Here’s why –
| For investors | For companies |
| You can earn a higher income on your investment. Dividend payments can create a supplemental source of income. You can reinvest the dividend into stocks or other investments to enhance your portfolio. | A high DPS depicts strong profitability. This enhances the company’s market value and boosts its perception among investors. It also shows that the management is confident about the company’s performance. The company can attract new investors. |
A low DPS usually means low profitability. This, in turn, means that the company is not performing well. However, a low DPS is not always a negative sign. If a company is expanding, it might retain a larger portion of its profits and pay limited dividends. In such cases, the DPS would be low (but the company could have good future prospects).
So, you should assess the complete financial picture of a company and not judge it by its DPS alone.
Conclusion
Companies can choose to declare dividends from the profits they make, which can be of various types. The dividend per share is the dividend shareholders receive per unit share. It can be calculated through formulas and is also mentioned in official communication and documents like the financial statements of a company. You can analyse the DPS before investing in a company.



