IPOs (Initial Public Offering) are a rage in today’s investing world. The year 2022 saw some major IPOs, with LIC topping the buzz charts. More than 60 companies went public in 2021, raising trillions. The trend is only expected to grow further. But what are IPOs?
In an IPO, a private company becomes a public company by raising capital from the public. Let’s understand the basics of an IPO and how it works.
IPO meaning
In an IPO, a private company floats its shares to the public for the first time to raise money and list them on the stock exchange.
Companies use an IPO to acquire fresh capital, which can be used for different purposes like research and product development, improving distribution channels, expansion, acquisition and even debt settlement.
IPO: Key Points to Remember
- An IPO allows a private company to become public by issuing shares through a stock exchange.
- The company submits key documents related to its earnings to the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) before the IPO is announced.
- Once the company is listed on the stock exchange, its shares can be traded in the share market.
How does an initial public offering work?
A company must follow a standard set of protocols and procedures if it wishes to go public.
The company must first engage an underwriter or an investment bank for a value assessment. Based on the assessment, the company can decide the price band and the number of shares to issue to the public.
The underwriter then sends an application to SEBI to verify all the information. SEBI directs the company to release a Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP). The prospectus contains all the details about the company, its financials etc., that are important for the investors.
The history of IPOs
The practice of conducting the IPOs began in the Netherlands when the Dutch East India Company offered its shares to the general public in 1602. Since then, several companies worldwide have used IPOs to raise capital and pursue growth.
Reliance Industries Limited was the first Indian company to launch its IPO in 1977. The company had issued 2.8 mn equity shares valued at Rs. 10 each.
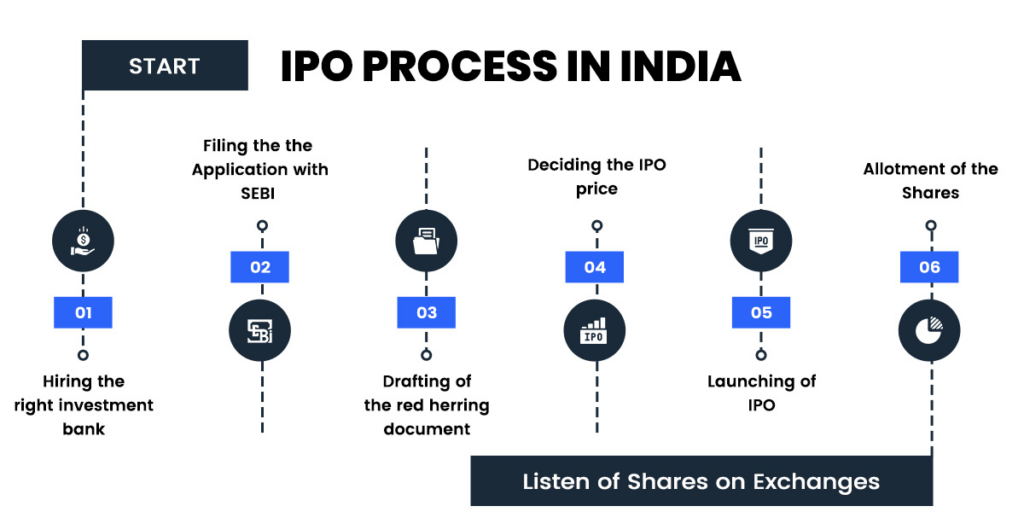
Steps to an IPO
An IPO is a lengthy process involving several steps. Some of these steps include
- Proposals: Several underwriters and investment firms submit their proposals to the company.
- Choice: Once the private company goes through all the proposals, it decides on the underwriter and gets into an underwriting agreement.
- Formation of an IPO team: The team consists of underwriters, Chartered Accountants (CAs), finance associates, etc.
- Documentation: The application is drafted, which includes financial statements, growth strategy, net worth, etc.
- Marketing: The company releases material to generate positive headlines and demand. The shares are marketed to the public, and once underwriters gauge demand, they can change the company’s valuation along with the share prices.
- Verification: SEBI goes through all the documents to ensure that all the eligibility norms are being adhered to.
- Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP): Once SEBI approves the documents, it directs the company to release its DRHP. The prospectus states the number and price of each share that will be offered through the IPO.
- The IPO: The IPO opens for a 5-6 day bidding window during which investors are allowed to bid
- Allotment: Investors, based on a lottery system, are allocated shares, which are credited to their Demat accounts. Other investors receive a refund.
Advantages and disadvantages of an IPO
Investors find IPOs advantageous because they get the chance to buy shares before market forces have the opportunity to drive prices up. Many investors also feel like this is the point of maximum transparency – where institutional investors (investment banks etc.) and retail investors have access to the same amount of information.
The disadvantages of investing in an IPO are the lack of historical stock price data and the chance that you might not receive the allocation you bid for.
Key terms in IPO
There are several terms that you might come across in an IPO discussion. Some of these terms include
- Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP): This document contains all the information about the company that investors need to make a sound decision. It includes the company’s valuation, share price, strategy for utilisation of IPO proceeds and other key details.
- Price band: This is the range within which the investors can bid for the shares. The band is decided mutually by the company and the underwriter.
- Offer date: This is the date investors can apply to buy IPO shares.
- Minimum subscription: This is the minimum amount the company must raise through their IPO, failing which all capital must be returned. In India, the minimum subscription rate is 90% of the issued share capital.
- Issue price: The price at which the shares are allotted to the investors is called the issue price.
- Oversubscription: This happens when the bids for shares exceed the number of shares floated in the primary market.
What is the difference between IPO and share?
Let’s check the differences between an IPO and a share:
| IPO | Share |
| IPO is the process by which a company goes public | A share is a portion of ownership in a public company |
| The price may be fixed, or there might be a price range | The market decides the price |
| Investor may or may not receive shares bid for | Investor get shares provided they are willing to pay the price |
| Past share price is not available | Investors can access the past share price |
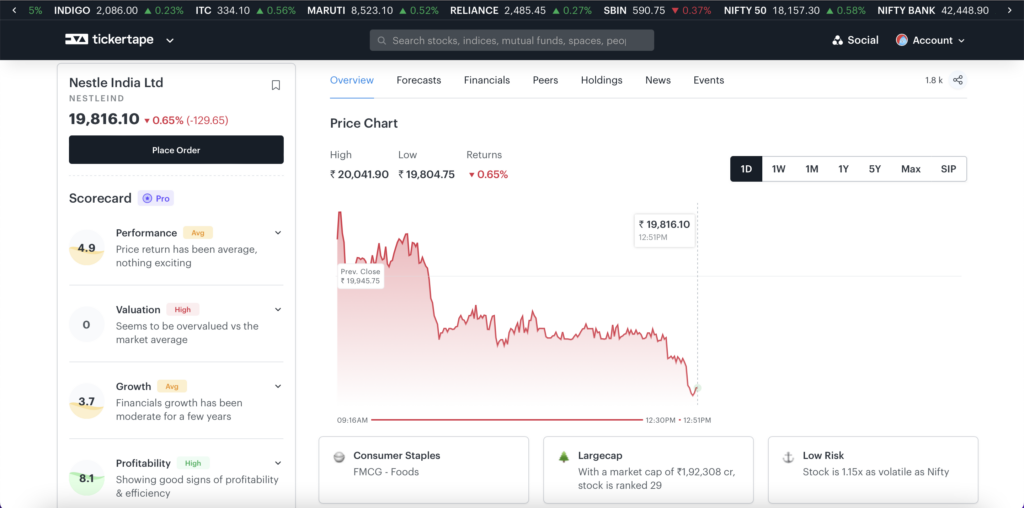
To find the current price of the stock, use Tickertape’s Stock Pages. Not just the stock price, you can also get several other details about a company like its 1-yr returns, 5-yr CAGR, financials, market cap, with other key metrics. And most importantly, there is a Scorecard which can determine the performance of a stock.
Conclusion
An IPO plays a major role in the transition from a private company to a public company. If a company wants to raise capital from the general public and get listed on the stock exchange, it launches an IPO. Once the IPO is announced open, investors can bid for the shares. But, remember, stocks carry high risk. Consult your advisor before applying for an IPO.



