Accounts payable refers to short-term payments owed by a business to its suppliers, which are shown as a liability on a company’s balance sheet. For example, if a company purchases goods or raw materials on credit which needs to be paid back in a short period of time, it is called accounts payable. In essence, accounts payable are the sum of all amounts owed to vendors.
For business accounts payable management is critical for managing a business’s cash flow. Therefore, in order to run a business efficiently, we have explored deeper into the concept of accounts payable to understand its meaning, types and the accounts payable processes
You will Learn About:
What are accounts payable?

Accounts payables are a company’s outstanding obligations to its creditors or suppliers.
In other words, an account payable is a current liability/debt that a business owes to another business or entity or third party, typically one that is to be paid within a short period. Here, the third parties could be banks, companies, vendors and more.
Accounts payable appear on a company’s balance sheet, where it is categorised as a current liability. When a company buys more goods and services on credit, the accounts payable consequently increase. On the other hand, a decrease in accounts payable can indicate that the company is paying off its obligations faster than it is acquiring new credit.
Accounts Payable – Main Highlights!
- Accounts payable is an account that represents a company’s short-term debt to its creditors or suppliers.
- A company’s accounts payable appears on its balance sheet under the liabilities section.
- If the company increases its credit line, accounts payable will increase.
What are the types of accounts payable?
Payables are often categorised as trade payables (payables for the purchase of physical goods that are recorded in inventory) and expense payables (payables for the purchase of goods or services that are expensed).
However, there are other types, too, such as non-trade payables, taxes payable, loans payable, and wages payable. To delve deeper into the concept of payables, here’s the contrasting difference between different types of payables –
Accounts payable vs trade payable
Let’s look at the primary difference between accounts payable and trade payable, which are often used interchangeably.
| Trade payables | Accounts payables | |
| Definition | Trade payables are the money a business owes to vendors for inventory-related goods, which can include anything from office supplies to inventory. | Accounts payables include all your short-term debts or obligations, including trade payables. |
| Example | If a restaurant owes money to a beverage or food company for supplies, those items are considered part of the inventory and trade payables. | Since accounts payables are essentially bills that a company needs to pay, they include cleaning services, staff uniforms, and office supplies. |
Accounts payable vs accounts receivable
There could be some confusion when dealing with accounts receivable and accounts payable. They are both very similar in the way they are recorded. However, it is crucial to differentiate accounts payable and receivables.
As important concepts in accounting, the difference between payables and accounts receivables is that account receivables represent the money that is owed to a company for services that have been rendered. Accounts payables, on the other hand, represent the money that a company owes to third parties. This could be for the kind of payments that are due to suppliers or creditors.
It is noteworthy, though, that accounts payables are booked as liabilities, and account receivables are recorded as assets since the former is a liability, whereas the latter is an asset. Mixing the two up can result in a lack of balance in the accounting equation, causing errors in the financial statements.
Examples of payables
Some examples of payables include supplier invoices, legal fees, contractor payments, and so on. Additionally, it will also record purchases from a vendor on credit, a subscription, or an instalment payment (that is due after goods or services have been received).
How to record accounts payable?
Efficient double-entry bookkeeping mandates offsetting debit and credit entries recorded in the general ledger. This ensures that the books of accounts are always balanced and accurate. The process of recording accounts payable goes as follows –
- The accountant will credit the accounts payable the moment an invoice is received.
- The debit offset for this entry would go to the expense account for the goods or services purchased on credit or to the asset account if the item purchased was a capitalisable asset.
- The accountant decreases the liability balance by debiting accounts payable when the invoice is cleared. The cash balance reduces when the offsetting credit is sent to the cash account.
Can accounts payable qualify as business expenses?
Some people mistakenly believe that accounts payable only refer to a company’s day-to-day operational expenses. However, this is not the case.
Expenses are the costs that are incurred for the production of goods or services. Now, these expenses may not be paid immediately. On the other hand, accounts payable are a liability that has to be paid off in a short period of time.
Additionally, expenses are found on the income statement, while payables are booked as a liability on the balance sheet.
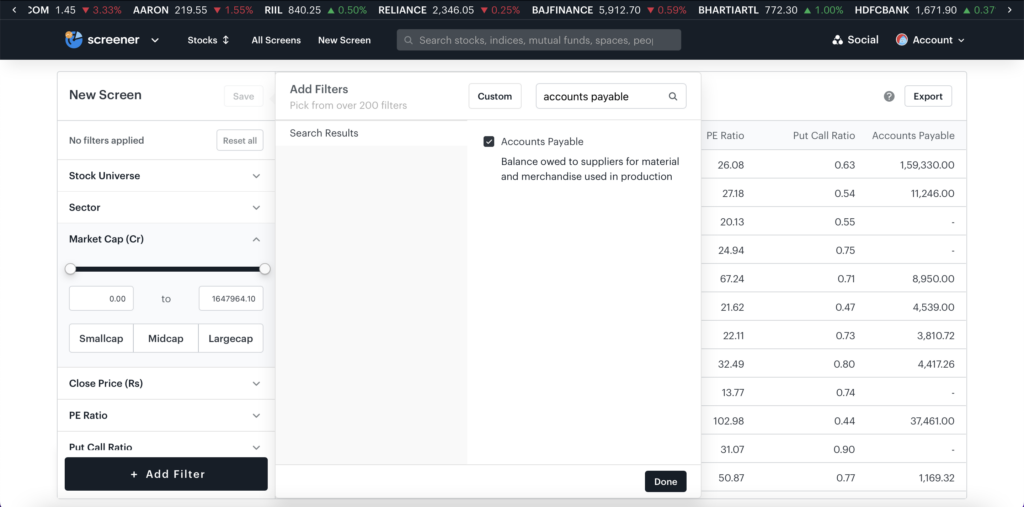
Using Tickertape Stock Screener to check a company’s accounts payable
Accounts payable can be found on a company’s balance sheet under current liabilities. This is because they represent funds that are owed to third-party entities. Use Tickertape Stock Screener to know the accounts payable of a company. Along with it, there are over 200 filters to help you find the best stocks.
Conclusion
Accounts payable refers to the outstanding obligations that a company has accrued from its business dealings that must be paid off in the near future. This usually includes money owed to suppliers, independent contractors, and other service providers. Ideally, the accounts payable turnover ratio should be high, implying that the business is paying off its debt quickly. It is important to understand the concepts of account payables to fully gauge the liquidity and current position of a company.



