There is no certainty about the stock prices. Feeling the market sentiment, they sometimes go up or fall. Therefore, understanding the volatility risk cannot be avoided while trading in stocks as different stocks have different volatilities. To measure the volatility of a stock investors use Beta.
Before we delve deeper into understanding how to calculate beta, let’s understand the concept of beta in detail.
You will Learn About:
What is beta in the stock market?
Beta in the stock market represents a stock’s volatility or systematic risk relative to the volatility of the stock market as a whole. In simpler terms, how a stock moves in relation to the market can be measured through beta.
Beta is used to measure risk and is an important part of the CAPM (Capital Asset Pricing Model).
For practical purposes, in India, returns from benchmarks like Nifty are considered when measuring beta as they reflect well the overall performance of the markets. The beta of benchmark indices is typically considered to be 1.0.
Beta – All You Need To Know!
- Beta is used to measure the volatility of a stock in relation to the overall market and its movements.
- Beta is a numerical value and can be equal to, greater than, or less than 1. Stocks with a beta value higher than 1 are considered high beta stocks, whereas those with less than 1 are considered low beta stocks.
- High beta stocks are more volatile than low beta stocks but can offer good returns. Low beta stocks are more stable in comparison to high beta stocks but may offer low returns.
- Alpha and beta are both used to determine the risk and return of an investment or stock. However, alpha measures the excess return of a stock over the benchmark, whereas beta measures the movement of a stock in comparison to a benchmark.
How to calculate beta?
The beta of a stock can be calculated using a simple formula. The beta formula is as follows –
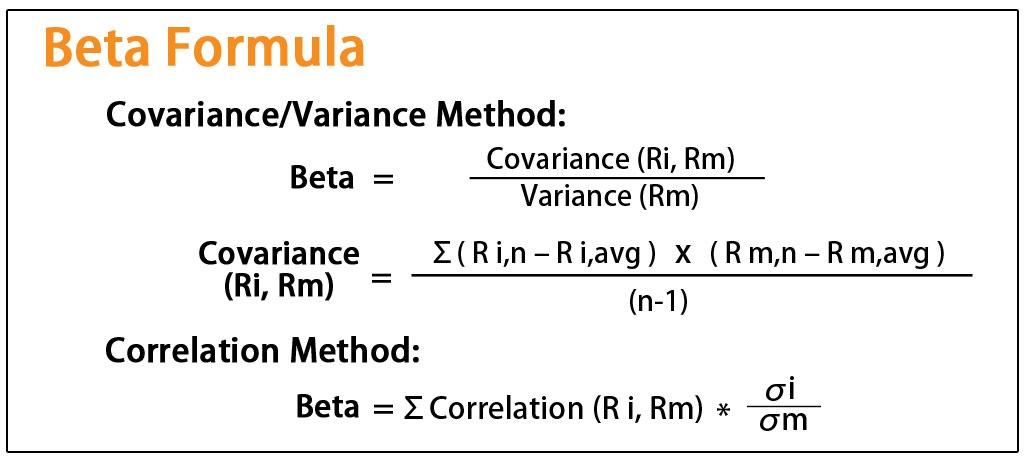
Beta (β) = Covariance (Ri, Rm) /Variance (Rm)
Here, Ri is the return from the stock
Rm is the return from the benchmark index/markets
Covariance of the stock and the markets
Variance of the market
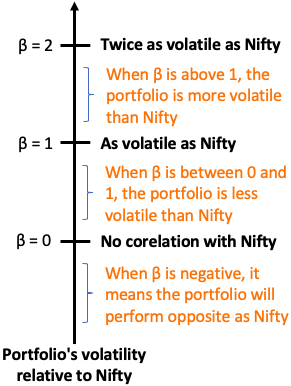
The beta value of a stock can be greater, lesser, or equal to 1. Here’s how to read these values –
- Beta higher than 1 – The stock is more volatile than the market. A slight change in the market indices will cause a considerable shift in stock prices.
- Beta lower than 1 – The stock is less volatile than the market. Any change in the market indices will not result in an equivalent change in the stock prices.
- Beta equal to 1 – The stock shares the same volatility as the overall market. Any change in the market indices will produce an equivalent change in the stock prices.
What are high beta stocks?
High beta stocks are those stocks whose beta is more than 1.
These stocks exhibit higher volatility and also have the potential to generate attractive returns in a bullish market.
Investors with higher risk tolerance can benefit from investing in high beta stocks during bull runs. Long-term investors can also benefit from investing in high beta stocks since the short-term volatility is ironed out in the long run.
However, it must be noted that these stocks decline beyond comparison when the markets crash. In other words, high beta stocks carry high risk and volatility and can result in losses if not managed actively.
In retrospect, small-cap and growth stocks generally depict high beta values
What are low beta stocks?
Low beta stocks are those that carry a beta value of less than 1.0.
They are less volatile than the market and are generally preferred by risk-averse investors. It is noteworthy that in turbulent markets, low beta stocks show higher stability. i.e., they are less impacted by market volatility.
Usually, large-cap companies have low beta values. Pharmaceutical, FMCG, and automobile stocks are also observed to have lower beta.
If you are looking to add low beta stocks to your investment portfolio, visit Tickertape Stock Screener and add ‘Beta’ filter to customise your search instantly.
Other beta values
Besides stocks, there are other market securities whose beta can be calculated. Securities such as mutual funds, ETFs, etc., can also have beta value higher than, lower than or equal to 1. However, in some cases, the beta can also be 0 or less than 0, i.e., in the negative.
Let’s understand what these two values mean –
- Beta equal to 0 – Beta value which is equal to 0 means that the security is not correlated to the stock market. It means that the value of the security will change independently of the stock market’s movements. Common examples include bonds, fixed deposits, and other fixed income saving instruments that are unaffected by stock market movements and, thus, have a beta of 0.
- Beta less than 0 – Securities with a negative beta depict an inverse correlation with the stock market. In simpler terms, this means that if the stock market rises, the prices of such securities might fall and vice versa. Gold is a common example of a security whose beta is usually negative. This is because when the stock market experiences considerable volatility and falls, investors consider gold to be a safe haven. They invest in gold to avoid losses from the stock market, and gold prices might then increase with increased demand.
Difference between Alpha vs Beta
While beta is an important metric to measure volatility, another metric that is commonly used by investors is called alpha.
Alpha measures the additional/excess returns a stock or a security yields over and above the benchmark returns. Alpha and beta are both used to analyse stocks when measuring their inherent risks and returns. However, both concepts are different.
Here are a comparative analysis of alpha and beta to understand what each means and how one differs from the other –
| Points of difference | Alpha | Beta |
| Meaning | Alpha measures the excess returns delivered by a stock over the benchmark returns. | Beta is a measure of a stock’s volatility relative to the stock market’s overall volatility. |
| Value | It is read in percentage form (though it is numerical). | It is expressed in a numerical value |
| Measure | The minimum alpha of a stock can be zero, implying that the stock does not outperform its benchmark | The minimum beta can be below zero for securities that are negatively correlated with the market |
| Calculation formula | Alpha is calculated by deducting the expected rate of return from the current rate of return.α= Actual rate of return of portfolio – Expected rate of return from portfolio | Beta is calculated by dividing the covariance of the stock and the market returns by the variance of the market returns.β=Covariance (Ri, Rm) /Variance (Rm) |
Conclusion
When investing in stocks or any other market-linked securities, it is important to study their beta values, which measure the relative risk of the security in comparison to the whole market. If you have a high tolerance for risk, you should explore high beta stocks. On the other hand, if your risk tolerance is limited, and you want to maintain stability of your portfolio, you should explore for low beta stocks. Use alpha and beta together to estimate the risk-return trade-off of an investment. Then, assess your investment strategy and risk profile to pick stocks and create a diversified portfolio.
Did you Like the Explanation?
Authored By:
Hey there, I’m Harshit Singh Mahey! With eight years of experience as a Content Strategist, I’ve had the pleasure of working with a Fortune 100 company and building three successful startups from the ground up.
As an investment fanatic, I’ve dabbled in early-stage startups, mutual funds, gold, stocks, smallcases, and real estate to identify which assets generate the highest ROI. At Tickertape, I’m dedicated to presenting my learning and providing insightful suggestions to help my readers make sound investment decision.



