As a firm strives to grow its business, it may incur a wide range of expenses. This may include small or insignificant short-term costs and other considerable long-term expenses.
Capital expenditure essentially comprises the expenditure incurred by a firm to fund the purchase of new equipment and/or enhance long-term assets. In other words, company funds directed toward purchasing new assets are categorised under capital expenditure. These expenditures are usually added to the cost of the asset or recorded in the balance sheet rather than expensing off in the income statement.
Read further to know all about capital expenditure.
What is capital expenditure?
Capital expenditure (Capex) refers to the funds allotted by a company toward maintaining, enhancing and purchasing long-term assets with the aim of improving their capacity and efficiency.
Typically capital expenditure funds the purchase of long-term assets such as machinery, equipment, building, furniture etc. It also includes intangible expenses such as trademarks, patents or licences. In fact, even R&D may be accounted for under capital expenditure.
Capital Expenditure: All You Need to Know!
- Capital expenditure is the capital a business spends for purchasing, maintaining and improving its long-term assets. Such expenditures are irreversible and attract depreciation/amortisation costs.
- Capital expenditure differs from revenue expenditure, primarily in terms of expense and utilisation.
- Capital expenditure is accounted for on the asset side in the balance sheet and also depicted in the cash flow statement.
- Capital expenditure has numerous benefits, such as analysing free cash flow to the firm. However, some challenges in determining Capex include inaccurate data/projections.
Features of capital expenditures
Let us understand the different features of capital expenditures:
- Long-term effects
Decisions pertaining to capital expenditure generally tend to have long-term effects and will significantly impact a company’s future. A company’s budgeting process and long-term goals must be set before allocating capital expenditure.
- Irreversibility
Capital expenditure may be difficult to reverse without causing losses to the company. Suppose a company purchases machinery for its business, and it fails to meet the desired requirements. Even if the company decides to sell it back, it may not recover the entire cost.
- High initial costs
Capital expenditure comes with a substantial initial cost outlay to offer long-term benefits. Such cost shall be borne, keeping in mind the opportunity cost.
- Depreciation
As capital assets are used in businesses, the capital expenditure incurred is added to the cost of the asset. The depreciation on such expenditure begins promptly and extends throughout the assets’ useful lives.
Types of capital expenditures
Let us understand the two types of capital expenditures
- Maintenance expenditure
The expenses incurred in maintaining the current operating levels in a company, such as replacing old machinery with new ones or making additions to an existing property.
- Expansion expenditure
The expenses incurred to enhance future growth at the company. These may include purchasing new machinery with the latest technology, acquiring additional land or property, entering new markets, etc.
Capital expenditure examples
Let us look at some of the capital expenditure examples.
- A company runs a cement production business with an existing capacity of 400MT. To keep up with the market demand, it decided to open a new production unit with a capacity of 500MT. The new unit will help the company in the long term and falls under capital expenditure.
- A company acquiring new equipment or technology to manufacture a vaccine or for R&D can also come under capital expenditure.
Differences between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure
The primary difference between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure is that the expense incurred is long-term in the case of capital expenditure, while the reverse is true for revenue expenditure.
Let us understand in detail how these expenses differ.
| Characteristics | Capital expenditure | Revenue expenditure |
| Definition | These are expenses incurred for upgrading or purchasing assets. These expenditures are added to the cost of the asset and recorded in the balance sheet. | These are expenses incurred for day-to-day business activities and are charged to the income statement as and when they are incurred. |
| Duration | The expenses and benefits are usually long-term. | The expenses are short-term, and the benefits are limited to the current accounting year. |
| Frequency | These expenses are usually non-recurring. | These expenses are incurred frequently. |
| Depreciation | Each year, depreciation is charged on capital expenditure. | Revenue expenditure is free of depreciation charges. |
Accounting for capital expenditure
Capital expenditure is accounted for in the balance sheet. It is also recorded in the cash flow statement under “Cashflow from Investing Activities” in the financial period it occurs. Since cash is spent for this expenditure, it is treated as an outflow in the cash flow statement.
Capex formula
The formula for Capex is as follows –
Capex = Net increase in PP&E + Depreciation expense
Here, PP&E stands for Property Plant and Equipment
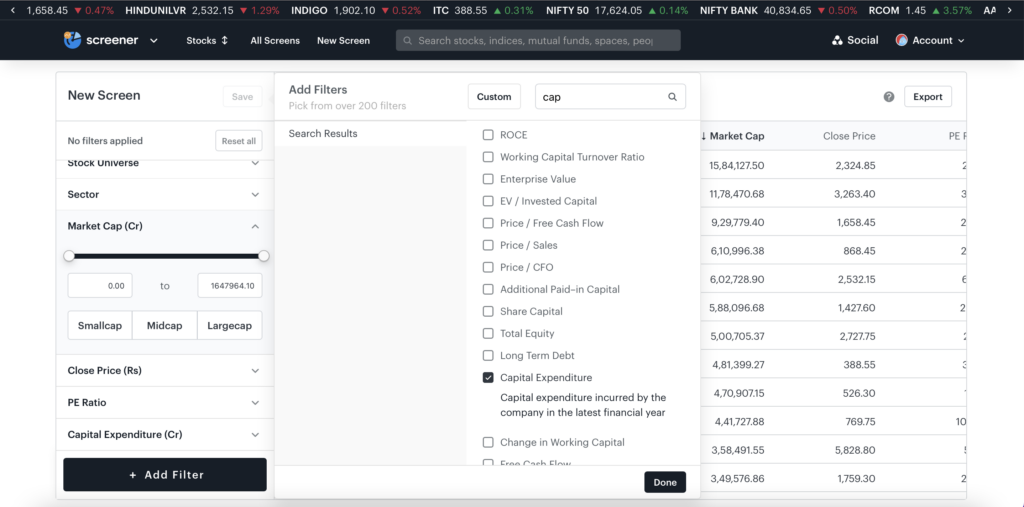
Use Tickertape Stock Screener to find the capital expenditure of a company. Along with capex, you can use 200+ filters to analyse a stock and find the best ones.
What are efficient capital expenditure budgeting practices?
- Planning
The first and most critical step in Capex budgeting requires companies to lay out a clear and concise plan of their future goals and a well-defined project scope.
- Budgeting
For better resource management, it is ideal to have separate budgets for capital and revenue expenditures.
- Limit
It is essential to set a budget limit for capital expenditure for companies to account for and manage any financial risk.
- Monitoring returns
Capital expenditure must be monitored at regular intervals to ensure the company has received the desired results.
Additionally, a company can adopt the bottom-up approach. This ensures that all the concerned departments contribute to the budgeting process, which helps better utilise resources. Also, firms should focus on capturing accurate data from different departments to effectively monetise capital expenditure.
How to manage your capital expenditures?
It is crucial to manage capital expenditure effectively. Here are a few guidelines describing how companies can manage their capital expenditure.
- Long-term objectives
The first step in managing capital expenditure is to clearly define long-term goals and objectives.
- Expense requests
It is ideal to have a well-structured framework for cost-benefit analysis and to establish an expense approval framework.
Lastly, note that you cannot write off capital expenditure expenses immediately. Instead, a regular depreciation will be levied on the purchased capital. Companies should keep this in mind to better manage finances.
Importance of capital expenditures
The importance of capital expenditures is outlined below:
- The assets purchased help in generating long-term benefits for the company.
- It can help analysts gain insight into the firm’s investment activities.
- Capital expenditure is useful in calculating free cash flow for the firm.
Challenges with capital expenditures
The challenges companies face related to capital expenditures are mentioned below:
- Measurement
Companies often face problems when it comes to accurately measuring the costs involved.
- Unpredictability
Uncertainties in the cost-benefit analysis may result in the desired outcome not meeting the projections.
- Temporal speed
The capital expenditure costs and the associated benefits rely on considerable timeframes. This causes difficulties while establishing equivalence and estimating discount rates.
Conclusion
Capital expenditure is required to maintain and enhance a company’s operations. The requirement of capital expenditure can vary depending on the company’s requirements and the nature of its business. Some businesses may be more capital-intensive than others. Efficient planning and management of capital expenditure budgeting help companies manage their operations effectively.



