When you invest in mutual funds or any other pooled investment avenue, you will come across the term ‘expense ratio’. Though expressed as a percentage, the ratio depicts the overall expenses on the fund you have invested in.
Let’s understand what the expense ratio is all about.
You will Learn About:
What is an expense ratio?
The expense ratio is the overall charge of handling and managing a pooled fund. The asset management company (AMC) considers the overall expenses incurred in collecting investments from a pool of investors, creating a pooled corpus, allocating the corpus into different securities and managing it to generate returns.
These expenses are then aggregated to compute the expense ratio. Thus, in other words, the ratio represents the annual fee that you pay the AMC for handling and managing the pooled investment.
Expense Ratio – All You Need To Note!
- The expense ratio depicts the overall annual expenses of managing a fund in the case of pooled investments.
- The ratio is calculated by dividing the overall expenses by the average portfolio value.
- SEBI has limited the maximum expense ratio that mutual funds can charge.
- Expense ratio affects the returns. The higher the expense ratio, the lower would be the returns.
What are the components of an expense ratio?
While the expense ratio meaning includes all the expenses incurred by the fund house, broadly, there are three main expenses that a fund house incurs. They are as follows –
- Administrative costs
These are the costs incurred on administrative activities like maintaining records, sending communications to the customer, customer service, etc.
- 12-1b distribution expenses
These include the expenses incurred on promoting or advertising the fund. Moreover, if there’s a middleman involved, the commission payable to him is also included in this category.
- Fund management fee
The AMC appoints experienced fund managers to manage your investments. These managers are paid a salary which forms a part of the fund management fee.
How is an expense ratio calculated?
In simple terms, the annual expense ratio is calculated by dividing the aggregate expenses of the fund by the average portfolio value. The result is expressed in a percentage which depicts the expense ratio.
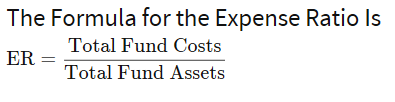
The expense ratio formula is as follows –
Expense ratio = Overall expenses of the fund/Aggregate portfolio value * 100
Here’s an expense ratio example –
Say a portfolio is valuing Rs. 10 cr. incurs an overall annual expense of Rs. 10 lakh. The expense ratio of the fund would be calculated as follows –
Expense ratio = Rs.10 lakh / Rs.10 cr. = 1%
Alternatively, use Tickertape Mutual Fund Screener to get the expense ratio of a fund. You can sort the list of best mutual funds using 50+ filters.
What is a good expense ratio?
There is no one particular figure that is considered to be good. When it comes to expenses, the lower, the better. In fact, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has the maximum expense ratio that mutual funds can charge. It is as follows –
| Assets Under Management | Equity mutual funds | Debt mutual funds |
| Up to Rs. 500 cr. | 2.25% | 2% |
| Rs. 500 to Rs. 750 cr. | 2% | 1.75% |
| Rs. 750 to Rs. 2,000 cr. | 1.75% | 1.5% |
| Rs. 2,000 to Rs. 5,000 cr. | 1.6% | 1.35% |
| Rs. 5,000 to Rs. 10,000 cr. | 1.5% | 1.25% |
| Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 50,000 cr. | Starting at 1.5%. Thereafter, the ratio reduces by 0.05% for every Rs. 5,000 cr. increase in the AUM. | Starting at 1.25%. Thereafter, the ratio reduces by 0.05% for every Rs. 5,000 cr. increase in the AUM. |
| More than Rs. 50,000 cr. | 1.05% | 0.80% |
How do expense ratios work?
The expense ratio can be understood as the cost of owning a fund and enjoying its returns. It is your contribution towards the costs that the fund incurs in managing your investments. Pooled investment avenues give you the benefit of –
- Investment in a large number of securities
- Professional fund management
- Diversified portfolio
- Readymade basket of securities
For these benefits, you pay a cost to the AMC, which is expressed in terms of the expense ratio.
All the costs that the funds incur are divided by the overall portfolio value to find the expense ratio. This ratio is applied to all investors and affects the returns you earn from the scheme.
How do expense ratios affect returns?
The expense ratio directly impacts returns. The total expenses are deducted before the returns are calculated from the portfolio value. As such, higher expense ratios mean higher expenses. Higher expenses, on the other hand, convert to lower returns.
For example, say the expense ratio of Fund A is 1.5%, and that of Fund B is 1%. As such, fund A would have higher expenses and lower returns compared to Fund B.
What should you consider about expense ratios?
Here are some aspects of expense ratios that you should know –
- Actively managed funds have higher ratios compared to passively managed ones.
- Funds that have a higher AUM can spread out their costs over a larger portfolio. As such, they have lower ratios.
- Always compare the expense ratios across similar funds. Choose a fund that has a lower ratio so that you can get higher returns.
- In the case of mutual funds, opt for direct mutual funds rather than regular ones. This is because direct funds don’t include commissions payable to middlemen. As such, their expense ratios are lower.
Conclusion
The expense ratio is an important indicator of the overall expenses of a fund. The higher the ratio, the higher the expenses and vice-versa. When investing in pooled avenues like mutual funds, ETFs, hedge funds, etc., look for funds with lower ratios so that you can enhance the return potential. Also, compare similar funds with the same investment objectives for best results. Choose suitable funds with lower expense ratios and build up a diversified portfolio.
FAQs
Did you Like the Explanation?
Aastik Chhabra



