Mutual funds receive a fair amount of interest from investors as an alternative to direct stock investing. This is primarily because they have the potential to generate market-linked returns while also offering the benefits of diversification (depending upon the mutual fund you invest in). They can also mitigate risks to some extent as they are managed by professional fund managers.
In this blog, we delve deeper into understanding what mutual funds are, different types of mutual funds, and how mutual funds are different from SIP.
What is a mutual fund?
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from investors and invests it in securities of various kinds, such as stocks, bonds, and other assets.
The combined profits from these investments represent the overall profit made by the fund’s investors. Each individual investor’s buy stake in the mutual fund schemes and take-home profit depends on the number of units of the mutual fund they hold.
Mutual funds are managed by professional managers whose goal is to generate income for the fund’s investors. Therefore, the portfolio composition of a mutual fund scheme is essential to note before investing in any mutual fund.
Return on equity: Highlights
- Mutual fund investment involves pooling investments from a large number of investors and investing the pooled corpus in securities and other market-based financial products.
- They can generate returns linked to the market and have the potential to generate higher returns than fixed income.
- Mutual funds are classified into different types based on the asset classes they invest in, their structure, their market capitalisation, etc.
- The real returns generated by a mutual fund depend on transaction charges and expense ratios.
Types of mutual funds
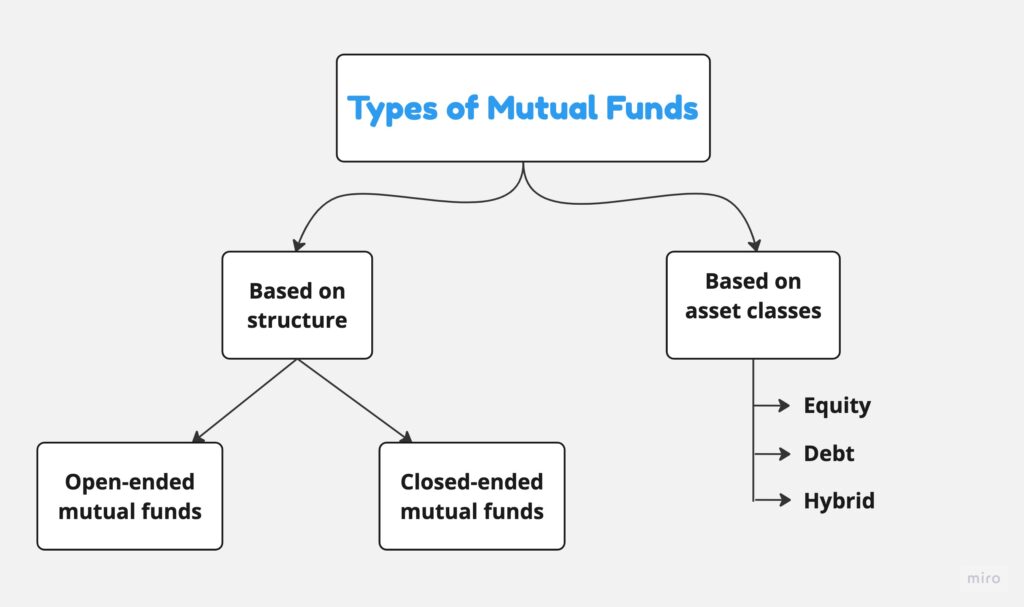
Mutual funds are classified based on how they are constituted, the kinds of securities they hold in their portfolio, their investment approaches, and so on.
Classification according to structure
- Open-ended mutual funds
These mutual funds allow investors to invest in them and redeem their investments at any time.
- Closed-ended mutual funds
Closed-ended mutual funds can be subscribed to only during new fund offer (NFO) periods. Moreover, investments in them are locked in until specific maturity dates.
Classification based on asset classes
- Equity mutual funds
Equity mutual funds invest at least 65% of their corpus in stocks of publicly traded companies. They have the potential to provide higher returns, but they also have an increased risk associated with them.
- Debt mutual funds
Debt mutual funds tend to invest mainly in fixed-income instruments like government securities, corporate bonds, corporate papers, etc. These can provide more steady returns than equity mutual funds and are less risky.
- Hybrid mutual funds
Hybrid mutual funds invest in both stock and debt instruments in variable quantities based on the fund’s investment objectives.
Advantages of investing in mutual funds
Some advantages of mutual funds are:
- Diversification
- Expert financial management
- Cost-effectiveness
- High liquidity (unless they are Equity Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS) funds that are come with a 3-year lock-in period)
- SIP option
Disadvantages of investing in mutual funds
Nevertheless, mutual funds do have some drawbacks as well:
- Transaction charges and expense ratios (i.e. the fees charged by an AMC for managing a fund); such fees reduce the real returns generated by a fund
- A relatively high level of dependence on good management
- The possibility of ineffective trade executions, resulting in sub-optimal gains
Who should invest in mutual funds?

- Mutual funds are traditionally designed to be long-term investments. However, there are also short-term and ultra-short-term options available. This makes them suitable for investors with all investment horizons.
- While risk is minimised through the presence of a fund manager and diversification, mutual funds are essentially market-linked products and therefore have inherent risks. Thus, they are only suitable for investors with a certain risk appetite.
How to invest in a mutual fund?
You can make a lump sum investment in mutual funds or choose SIP for periodic investments. Once you’ve decided the way you want to invest and the fund, you can invest as per the ways below:
- Online or offline from the mutual fund house directly
- Through your broker
- Through AMFI registered agents
You can use Tickertape Mutual Fund Screener to find the best mutual funds in India. You can filter the funds based on your preferred parameters like AUM, NAV, 1-yr returns and more. You can also download the list of funds filtered as per your preferred parameters.
The best part is you can watchlist your favourite funds to monitor them regularly. Click to learn more about how to use Tickertape Mutual Fund Screener.
Key terms in mutual funds
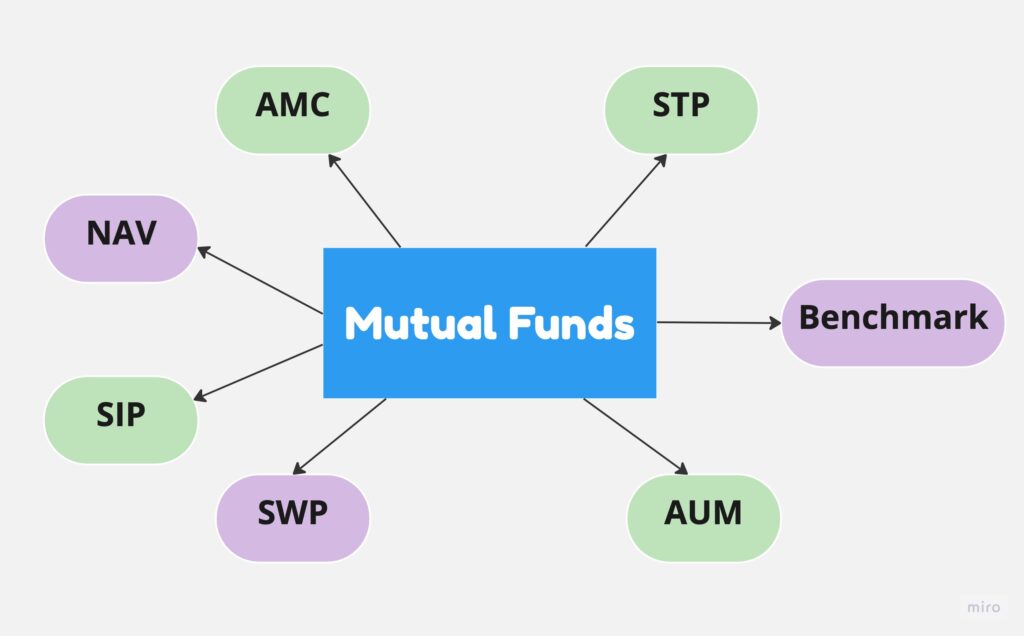
Before investing in a mutual funds, it is essential to know some common terms used in the context of mutual funds.
- AMC (Asset Management Company) – AMC pools money from investors and invests the same in various securities.
- NAV (Net Asset Value) – The NAV of a fund is the per-unit price of a mutual fund as determined by market forces by the end of each trading day.
- SIP (Systematic Investment Plan) – This type of investment option allows you to invest a pre-decided sum of money regularly.
- STP (Systematic Transfer Plan) – An STP provides an investor with the option to move a pre-decided amount of money from one fund to another within the same AMC over a period of time.
- SWP (Systematic Withdrawal Plan) – An SWP allows investors to withdraw their accumulated funds in small quantities over a predetermined timeline.
- Benchmark – Benchmarks are typically stock market indices that individual mutual funds compare themselves against to measure their performance. Actively managed mutual funds try to outperform various benchmarks, while passively managed mutual funds aim to match certain benchmarks.
- AUM (Assets Under Management) – This is the total amount of assets an AMC has under its control.
Conclusion
A mutual fund is a versatile investment choice that can help investors gain profits and build wealth by tapping into the opportunities presented by the markets. Mutual funds offer plans for every investor to meet varied short-term and long-term goals. The benefits of diversification, flexibility to invest relatively low amounts, and access to expert fund management services are some advantages of mutual funds that attract investors to them.



