Shares, also called equity, represent part-ownership in a company. They are increasingly gaining popularity among investors as they explore the stock market as an avenue to grow wealth.
Now with quick access to the internet and online brokerage services, you can invest in any share in just a few minutes! Read further to understand the definition of shares, types, features and more.
You will Learn About:
What are shares?

Shares are per unit capital of a company. When a company needs funds for growth or expansion, it can offer shares to investors.
These shares represent part-ownership in a company. Whenever you buy shares of a company, you become a shareholder of the company. Here, you are entitled to dividends and other benefits.
Return on equity: Highlights
- Shares denote part ownership in a company
- Equity shares and preference shares are the two main types of shares that companies issue
- Both equity and preference shares are further sub-divided into different types
- Companies issue shares to raise funds for their growth and development
Features of shares
Some of the salient features of shares are as follows –
- The value of shares is determined based on the demand and supply in the market. It constantly fluctuates
- Few shares may allot you voting rights
- Shares are perpetual in nature, i.e., they do not have a specific maturity date
Types of shares

Broadly, shares can be divided into two main categories: equity and preference. Let’s read each type in detail.
Equity shares
Equity shares are the most common types of shares that are offered by companies. Also called ordinary shares, equity shares form the bulk of the share capital of a company.
Features of equity shares
Common features of equity shares are as follows –
- Equity shares are issued at face value, but they trade at market value.
- A company issues equity shares in the primary market through an IPO (Initial Public Offering). After the shares are subscribed, and the company is listed, the shares trade in the secondary market, which is the stock market.
- Equity shares carry a high level of investment risk.
- Dividend income is a possibility if the company earns profits in a financial year and distributes the same among its shareholders.
Types of equity shares
Equity shares are subdivided into various types based on broad parameters. Let’s understand each of them.
Classification based on share capital
Depending on the share capital that they represent, equity shares can be divided into the following types:
| Types of equity shares | Meaning |
| Authorised share capital | The maximum capital a company can raise by issuing equity shares is called authorised share capital. |
| Issued share capital | Issued share capital is the capital raised by issuing a specific number of equity shares to the public for investment. |
| Subscribed share capital | Subscribed share capital is the part of the capital for which the company has received subscriptions from investors. It is a part of the issued share capital. |
| Paid-up share capital | The portion of the capital for which the investors have invested is called the paid-up share capital. This is a part of the subscribed share capital. |
Classification based on returns
Depending on the type of returns, equity shares can be sub-divided into the following types:
| Types of equity shares | Meaning |
| Dividend shares | Shares that give regular dividends are called dividend shares. |
| Growth shares | If the company reinvests the profits and does not declare dividends, it can use the same for growth. This growth leads to an increase in the market value of shares. Such shares are called growth shares. |
| Value shares | Value shares are those that trade on the market at a discount in comparison to their intrinsic value. |
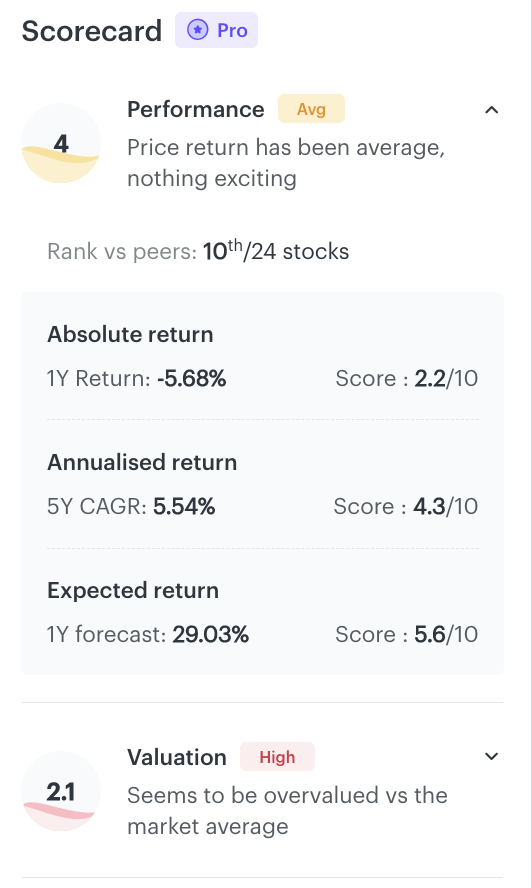
You can also use the Scorecard feature on Tickertape to gain more information about the stock.
Other types of equity shares
| Types of equity shares | Meaning |
| Bonus shares | Shares issued to existing shareholders without a cost are called bonus shares. |
| Rights shares | Existing shareholders get the privilege to subscribe to the additional issue of shares through a rights issue. You can buy such shares at a preferential rate within a specified period. |
| Sweat equity | Sweat equity shares are issued to company employees to compensate them for their hard work and efforts. |
| ESOPs | Equity Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) are equity shares issued by companies as a part of employee compensation. ESOPs allow employees to buy the company’s shares at reduced rates, hold them through the vesting period and then sell them at a higher rate for earning returns. |
| Voting shares | Shares that earn shareholders the right to vote are called voting shares. |
| Non-voting shares | Shares that do not have voting rights are called non-voting shares. |
Preference shares
Preference shares are also part of the share capital of a company. However, holders of such shares get preference in dividend payments and also at the time of liquidation, hence the name.
Features of preference shares
Some of the salient features of preference shares are as follows –
- Preference shares are not commonly available on the stock exchange for trading
- In some cases, preference shares may promise fixed dividends
- Preference shares generally don’t allow voting rights
- At the time of liquidation, preference shareholders are given first preference
Types of preference shares
Here is a look at some of the different types of preference shares issued by companies –
| Types of preference shares | Meaning |
| Cumulative and non-cumulative preference shares | If there is no dividend declaration in a year, the dividend payment is carried forward to the next year in cumulative preference shares. Non-cumulative shares, however, do not carry forward dividends. |
| Participating and non-participating preference shares | Participating shares are entitled to surplus profits over and above the dividend declared. Non-participating shares do not receive any surplus profit. |
| Convertible and non-convertible preference shares | Shares that can be converted to equity shares (after specified conditions are met) are called convertible preference shares. Non-convertible shares cannot be converted to equity shares. |
| Redeemable and irredeemable preference shares | Redeemable shares have a fixed tenure, after which the company buys back such shares at a predefined price. Non-redeemable shares continue in perpetuity. |
Why does a company issue shares?
Companies issue shares primarily to raise capital for their operations, growth, and expansion. Companies can also issue equity shares for the following reasons –
- To raise capital for various operations
- To get listed in the share market
- To gain visibility
- To expand their market reach
Conclusion
Shares denote ownership in a company. The most common types of shares are equity and preference, which are further subdivided into many types based on various parameters such as returns, share capital, etc. Remember, equity investments are highly risky. Consult your advisor before investing in shares.




Test_Comment
Test comment from V